ASP.NET MVC
- MVC stands for Model-View-Controller. It is a software design pattern that was introduced in the 1970s. Also, the MVC pattern forces a separation of concerns, It means the domain model and controller logic are decoupled from the user interface (view). As a result maintenance and testing of the application become simpler and easier.
2) Explain the MVC design pattern? or What does Model-View-Controller represent in an MVC application?
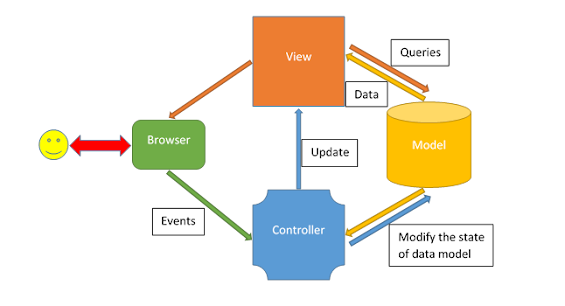
- MVC design pattern splits an application into three main aspects: Model, View, and Controller,
- Model: It represents the application data domain. In other words, applications business logic is contained within the model and is responsible for maintaining data
- MVC model is basically a C# and vb.net class. A model is accessible by both controller and view.
- A model can be used to pass data from controller to view. A View can use a model to display data on-page.
- View: It represents the user interface, with which the end-users communicate. In short, all the user interface logic is contained within the VIEW
- Controller: It is the controller that answers to user actions. Based on the user actions, the respective controller.responds within the model and choose a view to render that display the user interface. The user input logic is contained with-in the controller.
- Inside controller's, class action methods can be implemented which are responsible for responding to browser or calling views
- A controller can access and use a model class to pass data to views
- MVVM stands for Model-View-View Model. This pattern supports two-way data binding between view and View model. This enables automatic propagation of changes, within the state of view model to the View. Typically, the view model uses the observer pattern to notify changes in the view model to model.
- Model - The Model represents a set of classes that describes the business logic and data. It also defines business rules for data means how the data can be changed and manipulated.
- View - The View represents the UI components like CSS, jQuery, HTML, etc. It is only responsible for displaying the data that is received from the controller as the result. This also transforms the model(s) into UI.
- View Model - The View Model is responsible for exposing methods, commands, and other properties that help to maintain the state of the view, manipulate the model as the result of actions on the view, and trigger events in the view itself. In ASP.NET MVC, ViewModel is a class that contains the fields which are represented in the strongly-typed view. It is used to pass data from controller to strongly-typed view.
4) What is the advantage of MVC?
- Separation of concerns.
- Better support for Test-Driven Development.
- Clean URL.
- Better for search engine optimization.
- Full control over the user interface and HTML
- Loosely coupled so each component can be tested independently.
- The 3-layer architecture separates the application into 3 components which consist of the Presentation Layer, Business Layer, and Data Access Layer. In 3-layer architecture, the user interacts with the Presentation layer.
- 3-layer is a linear architecture.
- MVC architecture separates the application into three components which consist of Model, View, and Controller. In MVC architecture, the user interacts with the controller with the help of view.
- MVC is a triangle architecture.
6) What is the difference between asp.net MVC and asp.et webform?
|
ASP.NET Web Forms |
ASP.NET MVC |
|
Web Form follows a traditional event-driven development model. |
MVC is lightweight and follows MVC (Model, View, and Controller)
pattern-based development model. |
|
Web Form has server controls. |
MVC has HTML helpers. |
|
Web Form has state management (like as view state, session)
techniques. |
MVC has no automatic state management techniques. |
|
Web Form has file-based URLs means file name exist in the URLs must
have their physical existence. |
MVC has route-based URLs means URLs are divided into controllers and
actions and moreover it is based on the controller not on a physical file. |
|
Web Form follows WebForm Syntax |
MVC follow customizable syntax (Razor as default) |
|
Web Form, Web Forms (ASPX) i.e. views are tightly coupled to Code
behind (ASPX.CS) i.e. logic. |
MVC, Views, and logic are kept separately. |
|
Web Form has Master Pages for a consistent look and feels. |
MVC has Layouts for a consistent look and feels. |
|
Web Form has User Controls for code re-usability. |
MVC has Partial Views for code re-usability. |
|
Web Form has built-in data controls and best for rapid development
with powerful data access. |
MVC is lightweight, provides full control over mark-up, and supports many features that allow fast & agile development. Hence it is best for developing interactive web applications with the latest web standards. |
|
Web Form is not Open Source. |
Web MVC is an Open Source. |
7) What is the ViewModel in asp.net MVC?
- In ASP.NET MVC, ViewModel is a class that contains the fields which are represented in the strongly-typed view. It is used to pass data from controller to strongly-typed view.
- ViewModel contain fields that are represented in the view (for LabelFor, EditorFor, DisplayFor helpers)
- ViewModel can have specific validation rules using data annotations.
- ViewModel can have multiple entities or objects from different data models or data source.
- Routing is a pattern matching system that monitor the incoming request and figure out what to do with that request.
- At runtime, Routing engine use the Route table for matching the incoming request's URL pattern against the URL patterns defined in the Route table.
- You can register one or more URL patterns to the Route table at Application_Start event.
- ControllerName
- ActionMethodName
- Parameter
9) What is the difference between Routing and URL Rewriting?
- URL rewriting is focused on mapping one URL (new url) to another URL (old url) while routing is focused on mapping a URL to a resource.
- URL rewriting rewrites your old url to new one while routing never rewrite your old url to new one but it map to the original route.
 |
| URL Routing |
10) What are important namespaces in ASP.NET MVC?
- System.Web.Mvc -This namespace contains classes and interfaces that support the MVC pattern for ASP.NET Web applications.This namespace includes classes that represent controllers, controller factories, action results, views, partial views, and model binders.
- System.Web.Mvc.Ajax - This namespace contains classes that supports Ajax scripting in an ASP.NET MVC application.
- System.Web.Mvc.Html –This namespace contains classes that help render HTML controls in an MVC application.
11) What is View Engine?
- A View Engine is a MVC subsystem which has its own markup syntax. It is responsible for converting server-side template into HTML markup and rendering it to the browser.
- Initially, ASP.NET MVC ships with one view engine, web forms (ASPX) and from ASP.NET MVC3 a new view engine, Razor is introduced.With ASP.NET MVC, you can also use other view engines like Spark, NHaml etc.
12) What is Razor View Engine?
- Razor Engine is an advanced view engine that was introduced with MVC3.
- This is not a new language but it is a new markup syntax. Razor has new and advance syntax that are compact, expressive and reduces typing.
- Razor syntax are easy to learn and much clean than Web Form syntax. Razor uses @ symbol to write markup as:@Html.ActionLink("SignUp", "SignUp")
13) What is difference between Razor and WebForm engine?
|
Razor View Engine |
Webform View Engine |
|
Razor Engine is an advanced view engine that was introduced with
MVC3. This is not a new language but it is a new markup syntax. |
Web Form Engine is the default view engine for the Asp.net MVC that
is included with Asp.net MVC from the beginning. |
|
The namespace for Razor Engine is System.Web.Razor. |
The namespace for Webform Engine is System.Web.Mvc.WebFormViewEngine. |
|
The file extensions used with Razor Engine are different from Web
Form Engine. It has .cshtml (Razor with C#) or .vbhtml (Razor with VB)
extension for views, partial views, editor templates and for layout pages. |
The file extensions used with Web Form Engine are also like Asp.net
Web Forms. It has .aspx extension for views, .ascx extension for partial
views & editor templates and .master extension for layout/master pages. |
|
Razor has new and advance syntax that are compact, expressive and
reduces typing. |
Web Form Engine has the same syntax like Asp.net Web Forms uses for
.aspx pages. |
|
Razor syntax are easy to learn and much clean than Web Form syntax.
Razor uses @ symbol to make the code like as: @Html.ActionLink("SignUp", "SignUp") |
Web Form syntax are borrowed from Asp.net Web Forms syntax that are
mixed with html and sometimes make a view messy. Webform uses delimiters to make the code like as: <%Html.ActionLick("SignUp","SignUp")%> |
|
By default, Razor Engine prevents XSS attacks (Cross-Site Scripting
Attacks) means it encodes the script or html tags like before rendering to view. |
Web Form Engine does not prevent XSS attacks means any script saved
in the database will be fired while rendering the page |
|
|
|
- An HTML Helper is just a method that returns a HTML string.
- The string can represent any type of content that you want. For example, you can use HTML Helpers to render standard HTML tags like HTML , and tags etc.
- You can also create your own HTML Helpers to render more complex content such as a menu strip or an HTML table for displaying database data.
The HTML helpers that are mainly used to render HTML elements like text boxes, checkboxes, Radio Buttons, and Dropdown lists, etc. are called Standard HTML helpers.
List of Standard HTML Helpers
@Html.ActionLink() - Used to create link on html page @Html.TextBox() - Used to create text box @Html.CheckBox() - Used to create check box @Html.RadioButton() - Used to create Radio Button @Html.BeginFrom() - Used to start a form @Html.EndFrom() - Used to end a form @Html.DropDownList() - Used to create drop down list @Html.Hidden() - Used to create hidden fields @Html.label() - Used for creating HTML label is on the browser @Html.TextArea() - The TextArea Method renders textarea element on browser @Html.Password() - This method is responsible for creating password input field on browser @Html.ListBox() - The ListBox helper method creates html ListBox with scrollbar on browser
- Url helpers allows you to render HTML links and raw URLs. The output of these helpers is dependent on the routing configuration of your ASP.NET MVC application.
|
HTML Element |
Example |
|
Relative
URL |
@Url.Content("~/Files/asp.netmvc.pdf") Output: /Files/asp.netmvc.pdf |
|
Based
on action/controller |
@Html.ActionLink("About Us",
"About", "Home") Output: <a
href="/Home/About">About Us</a> |
|
Raw
URL for Action |
Url.Action("About", "Home") Output: /Home/About |
- AJAX Helpers are used to create AJAX enabled elements like as Ajax enabled forms and links which performs request asynchronously. AJAX Helpers are extension methods of AJAXHelper class which exist in System. Web. Mvc namespace.
The idea behind Unobtrusive AJAX is that AJAX behaviour is attached to form and anchor elements via HTML5 data-* attributes, instead of binding click event handlers in script blocks. In old MVC, these attributes can be generated from Html helpers: Ajax. BeginForm and Ajax.
- Layouts are used in MVC to provide a consistent look and feel on all the pages of our application. It is the same as defining the Master Pages but MVC provides some more functionalities.
@sectionis for defining a content are override from a shared view. Basically, it is a way for you to adjust your shared view (similar to a Master Page in Web Forms).
The
@RenderSectionsyntax goes into the Shared View, such as:
<div id="sidebar">
@RenderSection("Sidebar", required: false)
</div>
This would then be placed in your view with
@Sectionsyntax:
@section Sidebar{
<!-- Content Here -->
}- ViewData/ViewBag - Valid only for the duration of the current request.
You set it in a controller action and use it in the view, then it disappears.
The difference is that the first is a dictionary whereas the second is just a dynamic wrapper around this dictionary.Both point to the same data though.
- ViewBag was introduced in ASP.NET MVC 3.
public ActionResult Index()
{
ViewData["foo"] = "bar";
return View();
}
and inside the view you could use this value:
<div>@ViewData["foo"]</div>
Same with ViewBag but it is dynamic:
public ActionResult Index()
{
ViewBag.foo = "bar";
return View();
}
and inside the view you could use this value:
<div>@ViewBag.foo</div>
So as you can see ViewData/ViewBag are just an alternative way to pass information to a view from a controller action compared to the classic and recommended way which is using a view model:
public class MyViewModel
{
public string Foo { get; set; }
}
and then:
public ActionResult Index()
{
var model = new MyViewModel { Foo = "bar" };
return View(model);
}
and inside your strongly typed view:
@model MyViewModel
<div>@Html.DisplayFor(x => x.Foo)</div>
As you can see using view models provide a strongly typed approach in passing information to a view from a controller action.
- TempData - It allows for persisting information for the duration of a single subsequent request. You store something inside TempData and then redirect. In the target controller action to which you redirected you could retrieve the value that was stored inside TempData.
Example:
public ActionResult Foo()
{
TempData["foo"] = "bar";
return RedirectToAction("bar");
}
public ActionResult Bar()
{
var value = TempData["foo"] as string;
// use the value here. If you need to pass it to the view you could
// use ViewData/ViewBag (I can't believe I said that but I will leave it for the moment)
return View();
}
ASP.NET MVC will automatically expire the value that was stored in TempData once you read it. Under the covers ASP.NET MVC persists the information into the Session.
- Session - same as TempData except that it never expires - it will be valid for all requests, not a single redirect.
- ViewResult - Represents HTML and markup.
- EmptyResult - Represents no result.
- RedirectResult - Represents a redirection to a new URL.
- JsonResult - Represents a JavaScript Object Notation result that can be used in an AJAX application.
- JavaScriptResult - Represents a JavaScript script.
- ContentResult - Represents a text result.
- FileContentResult - Represents a downloadable file (with the binary content).
- FilePathResult - Represents a downloadable file (with a path).
- FileStreamResult - Represents a downloadable file (with a file stream).
- using System;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- using System.Linq;
- using System.Web;
- using System.Web.Mvc;
- using MvcActionSelectors_Demo.Models;
- namespace MvcActionSelectors_Demo.Controllers
- {
- public class DepartmentController : Controller
- {
- private readonly EmployeeContext _dbContext=new EmployeeContext();
- public ActionResult Index()
- {
- var department = _dbContext.Departments.ToList();
- return View(department);
- }
- [NonAction]
- public string HelloWorld()
- {
- return "<h2>Hello World, Welcome to programming.</h2>";
- }
- }
- }
ActionName attribute to the action method of the controller.[ActionName("PersonList")] public ActionResult Index(string txtKeyword = null) { return View(); }
- Razor code blocks are enclosed in @{ ... }
- Inline expressions (variables and functions) start with @
- Code statements end with a semicolon
- Variables are declared with the var keyword
- Strings are enclosed with quotation marks
- C# code is case sensitive
- C# files have the extension .cshtml
- Minimal or no code to create data-driven Web applications.
- Quick development time.
- Pages that are fully functional and include a display, insert, edit, delete, sorting, and paging functionalities.
- Built-in data validation that is based on the database schema.
- Filters that are created for each foreign key or Boolean fields.











No comments:
Post a Comment